One major challenge of near-term quantum computation is the limited number of available qubits. Suppose we want to run a circuit consisting of 400 qubits, but we only have 100-qubit devices available. What do we do?
Monday, 30 May 2022
At what cost can we simulate large quantum circuits on small quantum computers?
Sunday, 29 May 2022
Driving AI ethics for better business and a more just world
As AI technology pushes past limits in new real-world applications, regulators, investors, and the public are pushing back, asking what kind of relationship we ultimately want with AI and how to guarantee its responsible use. In response, organizations and institutions are embedding AI ethics into existing business guidelines. But a new report from IBM suggests there’s still a lot of work to do.
Alarmingly, only 40% of surveyed consumers say they trust companies to be responsible and ethical in their use of new technologies such as AI. Their doubts may be warranted, as fewer than 20% of executives strongly agree that company practices and actions on AI ethics match their organizations’ stated principles and values.
While traditionally delegated to technical leaders, the task of implementing an AI ethics strategy has dramatically shifted largely to CEOs, according to research conducted by the IBM Institute for Business Value.
There’s a growing recognition that AI is a cross-enterprise, multi-stakeholder endeavor. It’s more than just IT’s domain. HR, procurement and legal are all-in too. With AI encompassing both technical and non-technical solutions, it’s evolved to be business-led, requiring the most senior ranks to oversee its responsible curation.
An evolving framework for AI ethics builds social justice, equity, and trust
As AI extends into more and more institutions, ensuring trust and transparency of these systems will become critical to its success. In the courts, AI technologies can have even more far-reaching implications on citizens and institutions through predictive justice, the analysis of large amounts of data to make predictions on case outcomes.
One of the best examples of this can be found in New Jersey’s judiciary system, where algorithms review millions of case files to reduce bail decision bias. Not only did the system save USD 10 million, but it contributed to a 40% drop in the jail population with no measurable increase in crime rate. The system succeeds because there’s trust in the data and in the recommendations the system makes.
AI ethics are important for safeguarding democracy. And IBM’s study highlights it’s also good for business. According to the IBM research, organizations that place greater emphasis on AI ethics reported they have a greater degree of trust from customers and employees.
How IBM operationalizes trustworthy AI
IBM has a long-standing position that AI should be advanced responsibly in a way that ensures ethical principals at the technology’s core. This effort dates back to 2015, when world-renowned AI ethics researcher Francesca Rossi joined IBM, bringing 40 colleagues to help IBM embrace AI ethics as a core business tenet.To operationalize AI, IBM put principals of trust and transparency into place and formed an AI Ethics Board to review all AI efforts across the company. Today, it ensures that IBM-owned technology adheres to five pillars: transparency, explainability, fairness, robustness, and privacy. The company’s pioneering leadership is detailed in a 2021 World Economic Forum case study.
Put AI ethics into action
AI regulations are coming. And less than a quarter of responding organizations have operationalized AI ethics. The good news is that 79% of business leaders are now prepared to embed AI ethics into their AI practices. That’s up from 20% in 2018, according to the report, with over half now publicly endorsing common principles of AI ethics.
Getting to finish line takes a well-thought-out strategy: First, bring together a diverse set of stakeholders. Then build out an organizational and AI lifecycle governance. Finally, ensure interoperability so all ecosystem partners are on board. The sooner organizations get started the more global citizens can reap AI’s benefits.
IBM researchers discussed findings from IBM’s own AI ethics journey in this AI for Good webinar.
Watch this UNESCO-moderated discussion and interactive session with IBM Fellow and AI ethics leader Francesca Rossi, IBM Vice President and IBM Chief Privacy Officer Christina Montgomery, and IBM Distinguished Engineer Beth Rudden.
Source: ibm.com
Saturday, 28 May 2022
Get more value from your data with a data transformation roadmap
Data Economy - The Transformation Roadmap
So, how can you get the most value from your data? A knowledgeable and phased approach facilitates a smooth transition from legacy practices and products to processes that tap into the advantages of Canada’s data economy. Defining policies and roles, developing data-sharing control mechanisms, understanding existing and potential data across the company and beyond, and planning best use cases will lead to increased profitability, reduced operating costs, expanded products and services, and valuable insights to benefit you and your customers. And efficiently shared data promotes constructive collaboration with partners and stakeholders, both internal and external.
I recommend a three-step tactic of migration, modernization and monetization. Migration moves the data to the most appropriate cloud environment, or target state architecture, where core data models can be rebuilt and modernized, and then monetized through effective data and digital agile ecosystems that are ready for growth.
Here are two examples of the positive impact of data monetization in two very different industries.
Internal data monetization: an international airline launches a transformative journey
A large international airline needed to transition to a more streamlined technology landscape with an optimized operating model. Analysis of their current data landscape revealed multiple legacy applications that could not yield the insights required for their growth.
With guidance from IBM, the airline launched a Data Platform Stability and Modernization journey, migrating select on-premise data platforms and workloads to the cloud. Within the modernized data landscape, they could create models for customer and passenger data, then expand the insights to different lines of business, such as cargo, loyalty and commercial applications.
Their data modernization journey has realized three significant benefits. Revenue has been increased through their transformed data sources, channels and products. They have developed a data-driven decision-making culture through the resilient, cloud-based data environment. And their data security and governance has been improved, setting a foundation for realizing a good return on investment through further data monetization and data-sharing initiatives in the future.
External data monetization: Yara goes from bushels to bytes
“Agriculture is one of the last industries that has focused on systematic process optimization.” — Pål Øystein Stormorken, Yara
Norway-based Yara is the world’s largest fertilizer producer. It has established a solid reputation as a reliable source of information and a distributor of agricultural products, with an ethical and balanced approach to best practices for food production. Yara is dedicated to the exploration of new technologies that promote sustainable intensification to protect the environment, growing more food on existing farmland and avoiding deforestation. With the United Nations estimate that the population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050, along with alarming statistics on climate change and soil loss, Yara wanted to find solutions to the challenges to the food supply.
Yara partnered with IBM to build a digital farming platform with two new products: weather forecasting and crop-yield forecasting, following a pay-as-you-go commercial model. The cloud-agnostic strategy enables consistent data governance and data security, using DataOps to automate data functions so that its scientists could focus on data models and innovation.
The platform provides holistic digital services and instant agronomic advice around the globe, with the ability to reach 620 million farmers and serve up to 7% of the world’s arable land. These accelerators are just the first of many: an open innovation layer will allow Yara to create new revolutionary algorithms and a cognitive roadmap for farmers through constructive decision-making insights.
This is an example of the power of data monetization, generating not only business value, but also societal value in sustainable practices.
Your Opportunity
Canada will generate value for all of its citizens, industries, businesses and researchers by developing a flourishing data economy. IBM can help you understand and monetize your data, guiding you through your journey as you assess and prioritize your needs, select the right governance and operations models, and design a plan that propels you into the exciting future of data-driven innovation.
Source: ibm.com
Thursday, 26 May 2022
Unleashing end-to-end HR, mobility and payroll services to address talent challenges
IBM’s open ecosystem model is essential to bringing greater value to our clients, allowing us to deliver integrated solutions with speed and scale for true enterprise transformation. This is why the Global EY-IBM Alliance has expanded its focus to address our clients’ biggest challenge for talent: the urgency to attract, retain and upskill their workforce amid evolving employee expectations and a requirement for more engagement and consumer-grade experiences.
The EY-IBM Talent Alliance is not just another two-vendor model. EY and IBM have developed joint offerings and established a new Center of Excellence to address clients’ most pressing HR transformation needs. By combining EY and IBM’s consult-to-operate process and technology expertise, we create a truly unparalleled level of end-to-end services. Let me give you some concrete examples:
◉ For Human Capital Management (HCM) platforms like Workday and Oracle, EY and IBM amplify the value of clients’ HR Cloud Transformation by starting with a digital-first and human-centered design, accelerating implementation by 3x with ready-to-deploy assets, and leveraging data-driven AI to transform employee experience.
◉ For clients struggling with complex regulatory requirements and multi-vendor payroll systems with disparate data input and reporting methods, IBM and EY can provide advisory services and single-sourced payroll operations across 160 countries, all while reducing risk and saving time by leveraging Virtual Agents, pre-built payroll automated digital workers, and a suite of proprietary payroll technology.
◉ For clients looking to reduce operational costs and drive organizational resiliency, EY and IBM offer a holistic consult-to-operate solution for Recruitment Process Outsourcing, Mobility, and HR Outsourcing.
◉ And finally, underpinning the entire portfolio is our unique ability to create differentiated talent-focused technology offerings by combining EY’s assets around mobility and people experience with IBM’s talent AI microservices and deep expertise in platform strategy and hybrid, multi-cloud architecture.
Together we are better equipped to help our clients overcome the urgent need to attract, retain and upskill their workforce while transforming their HR function. The alliance offers an array of solutions including outsourcing to create space and free resources to focus on what matters most, laying the foundation for success with a strong HR Cloud Transformation program or applying AI and Automation technology to transform employee experiences.
And we are not just helping our clients transform; we apply these same principles ourselves. For decades, EY and IBM have partnered to help each other in talent-related challenges, including EY and IBM’s previous collaboration to introduce AI in Recruitment and reimagine employee assistance with the award-winning HR virtual assistant used in-house at both organizations.
Source: ibm.com
Tuesday, 24 May 2022
Three mega-trends shaping the data economy
Data Economy - A European Perspective
I recently had the pleasure of chatting with Vilmos Lorincz, Managing Director of Data and Digital Products for Lloyds Banking Group in the United Kingdom. Data is a fundamental currency in financial services, and so developing new approaches for banking protocols is critical to formulating progressive solutions for both clients and industry colleagues.
In response to a demand by the U.K. government for more transparency in financial services, the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) was set up in 2017 to deliver architectures that give customers more control of their data within a secure framework.
Lloyds Bank undertook a decisive transformation by moving their big data to the cloud and advancing data literacy for its employees, upgrading their capacity to provide benefit to clients. “We had to design the new agile operating model for more than a thousand colleagues,” said Vilmos, “helping them land in their newly defined roles, making the right technology investment choices, while engaging with more than 20,000 people.”
Vilmos emphasized that ethical behavior is absolutely critical to gaining and maintaining client trust, establishing a company’s brand as honest and responsible partners.
When asked about mega trends that are shaping the data-driven economy, Vilmos suggested three fundamentals.
1. Customer awareness: As citizens become more digitally sophisticated, they are keenly attuned to privacy and security issues. They rightfully want control of their data, expanding their ability to explore and select personal options.
2. Maturing corporations: The corporate world is advancing its ability to adopt new processes that keep pace with emergent technologies to add value to their business models and to benefit their customers.
3. Regulatory bodies: Regulators and governments are playing active roles in adjusting to new market realities, both protecting individual rights and positioning their nation to take full advantage of the opportunities of the rising data economy.
“Organizations are realizing that data is a mission-critical competitive factor and a must-have to meet and exceed customer expectations,” Vilmos explained. “They are becoming much better at deploying machine-learning and artificial-intelligence capabilities as an increasing part of their data estate.”
Vilmos advises business executives to prepare for a fast-evolving future by establishing frameworks that can accommodate the growth of the data economy and by planning how to deliver their products within the data-driven landscape.
Source: ibm.com
Monday, 23 May 2022
To reduce the environmental impact of your facilities, standardize sustainability data
Standardizing facility asset data and health assessment processes are critical steps to building a strong foundation for sustainability. As we work to achieve net-zero targets and carbon footprint reductions, we must prioritize deferred maintenance, capital projects, and programs backlog, and we must address the asset health and condition foundation for these decisions. By taking simple, consistent steps to maximize efficiency, we can systematize our knowledge to effect real change.
To make accurate comparisons of key assets that most impact sustainability measures (HVAC systems, lighting systems, etc.), we need to first identify those assets using standardized terms. Then we must assess their health using consistent procedures and risk ratings.
Read More: IBM Certifications
For example, one inspector calls an asset an “air handler” and collects information about the current flow rate for the unit she is inspecting. She notes the manufacturer, make, model, nameplate, age of the asset, and the most recent maintenance performed. This inspector also specifies special condition impacts of the rooftop location of the unit, as it exposed to sand and debris.
Another inspector calls a similar asset a “blower” and collects information about the manufacturer, make, model, nameplate, and age of the asset, but no other risk-related factors that impact its life. We have a disconnect on multiple levels: we cannot easily search and identify the two units because of the different nomenclature. We cannot make an informed hypothesis about early failure root-cause issues without additional follow-up inspections. And we have limited ability to prioritize higher or lower risk assets for future maintenance and eventual capital replacement.To solve these problems, we must first identify the full set of terms and needs in a consistent, standardized list. As we identify common opportunities, we can group projects to improve equipment purchasing leverage and parts and engineering services. These critical efforts will drive significant sustainability gains across organizations.
For example, one client recently embarked on re-lamping tens of thousands of stores to LED, saving millions through planned bulk purchasing. Rather than using the costly approach of having each store manager identify and manage individual LED lighting upgrades, this client was able to take advantage of huge energy savings across the store portfolio. This approach yields a one-time cost savings on the purchase and implementation program and long-term ongoing savings for energy usage.
With a mindful foundation, we can create more efficient systems that allow us to manage large facilities with fewer resources. Building consistent systems enables us to make clear recommendations for needed capital project investments, to prioritize those projects based on critical risk, and to impact compliance, and other cost-savings objectives. Most importantly, these foundations allow us to meet our maximum potential as contributors to a more sustainable future for our companies and our planet.
Source: ibm.com
Saturday, 21 May 2022
Business Analytics in the age of disruption
The 2020s have quickly been established as the age of the unexpected. Following the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations still find themselves needing to navigate unpredictable external forces that are largely out of their control, including labor disruptions, supply chain shortages, rising inflation and increased regulation. To navigate this constantly disrupted world, clients need more data, more collaboration and more assurances that they can act at the speed of business without risk.
In fact, everyone, at all levels, need to be data-driven to face this disruptive new reality. This situation persists across all areas of the business, and organizations have had to focus on new data applications to find a path towards success and resiliency. For example:
The most important types of analytics
Driving success with a winning combination
New packaging and integration
The Content Analytics Hub
Create a trusted data foundation with Cloud Pak for Data and IBM Data Fabric
Leading through a cycle of disruption
Tuesday, 17 May 2022
IBM Engineering Workflow Management is the tool of choice for the IBM zHW team
Imagine a digital engineering workplace where thousands of people are building a single system. This system is used by two-thirds of the Fortune 100, 45 of the world’s top 50 banks, 8 of the top 10 insurers, 7 of the top 10 global retailers and 8 out of the top 10 telcos as a highly secured platform for running their most mission-critical workloads. The development effort involves coordinating manufacturing, chip design, hardware, firmware, testing and defect tracking, while also meeting stringent regulatory requirements across a variety of industries and governmental standards.
This is the challenge that teams working on IBM Z® (the family name for IBM’s z/Architecture mainframe computers) face with every new product release.
Looking to the future
The IBM Z developers embarked on an extensive year-long evaluation of the development tools available in the marketplace that would help them manage their daunting engineering workflow. To carry out this evaluation, stakeholders created a matrix chart showing which solutions included the required integration capabilities for the tools used by the team.
The team selected components of the IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) solution, namely IBM Engineering Workflow Management (EWM), a fully integrated software development solution designed for complex product management and engineering, as well as for large, distributed development organizations that produce mission-critical systems subject to regulatory compliance. But this choice was not a foregone conclusion.
“By being completely objective and allowing the criteria and data to do the talking, we were led to EWM,” said Dominic Odescalchi, project executive manager of IBM zHW program management. “EWM was the consensus tool that we collectively agreed upon to provide the best solution.”
The advantage of IBM ELM tools
The zHW platform development team will leverage EWM as the central hub of engineering data, taking advantage of the customization capabilities within the broader ELM solution. This way, every team can adapt the processes that fit them best while remaining coordinated across one view of the development data and progress. Managing this data is critically important given the highly regulated workloads that are run on these systems across a variety of industries, governmental agencies and countries.
Given the holistic design of IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management, the team has also adopted the IBM Engineering Test Management tool to manage the comprehensive verification and validation of the hardware, again leveraging the one view and traceability across development data.
“With EWM’s integrated tool stack, key data will be readily available through connection to various team repositories,” said Odescalchi. “This will enable us to kick the doors wide open to automating and aggregating data. It’s going to free up countless hours to focus on performing higher value activities.”
Source: ibm.com
Saturday, 14 May 2022
How is SWIFT still relevant after five decades?
Too many people in the payments industry today hold the misconception that the SWIFT network is only for cross-border payments. This was indeed the case in 1973, when 239 banks from 15 countries joined forces to create an efficient, automated, and secure payments network.
At launch, the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) was built on three pillars, a secure and reliable communication protocol, a set of message standards and continuous new services aligning with its members’ needs.
A global network with a global reach
These pillars remain just as relevant 48 years later. So much more than a “cross-border payments network,” SWIFT has grown to serve more than 11,000 members in over 200 countries, providing a wide array of financial messaging services and influencing and innovating payments worldwide.
SWIFT has reimagined domestic high-value payments. Over 60 market infrastructures, covering 85 countries, rely on the SWIFT network to clear and settle domestic transactions. SWIFT FileAct, a bulk message exchange, allows correspondents to send and receive files mostly used to exchange bank statements or to exchange low-value, high-volume transactions.
SWIFT has extended the network to non-bank financial institutions, allowing the exchange of securities, foreign exchange and all other types of financial messages needed by its members. In fact, today more than 50% of messages on the SWIFT network involve securities trade transactions.
As the network expanded to cover most financial institutions worldwide, SWIFT opened its doors to large corporations such as Microsoft and GE. SWIFT became these companies’ single standardized connection to all their banks, adding efficiency and cost savings to treasuries worldwide.
Message standards and worldwide influence
From its inception, one of the key pillars of the SWIFT network is the message standard, a common language understood and processed by all its members.
The ISO 15022 standard, more commonly known as the SWIFT MT or Message Type standard, was introduced in 1995. It was similar in structure to that of the Telex technology that the network replaced. While it has evolved over the years, the MT standard remains the most used message format on the SWIFT network, and it has made its way to many domestic and private networks worldwide.
In the late 90s, SWIFT realized that the MT standard, although very useful, was restrictive in light of evolving technologies. SWIFT MT would not support the data that will be needed to be processed with each transaction. In 1999, SWIFT decided to adopt XML and develop a message standard that would recognize the richness of the data. ISO 20022 is often referred to as the “new standard.” But it was actually launched in 2004 in collaboration with SWIFT members. The new standard had some issues catching on, since adoption was voluntary and required heavy investment in backend systems, But on the heels of a 2019 mandate, ISO 20022 is now being deployed in every major network worldwide, and it is the foundation for interoperability.
Security
Given its prominence in finance, SWIFT has become a prime target for hackers. In fact, multiple hacking collectives have targeted the SWIFT network in attempts to divert funds. In 2016, hackers robbed over $80M from a large bank, money that today remains unrecovered. Although the network itself was not breached, SWIFT quickly realized that each of its 11,000 members did not meet industry standard security levels.
To level the playing field, SWIFT launched the Customer Security Program, a set of 27 security controls forcing each member to completely reassess its infrastructure, thereby securing the overall network. Within the first year, 91% of SWIFT members (covering over 99% of volume) had confirmed their compliance with the controls. This shows the influence the SWIFT organization has developed over the years to ensure compliance in a typically slow-paced industry.
Innovation
SWIFT has not rested on its laurels. The network is continuously focused on innovation to improve the member’s experience.
The SWIFT global payment innovation (SWIFT gpi) launched in 2017 with an objective to deliver cross-border payments faster, cheaper and with full transparency and traceability. Following a successful mass adoption of SWIFT gpi, over 90% of wire transactions were credited within 24 hours, including 40% credited within 30 minutes. SWIFT gpi is now extending its capabilities to reduce the number of rejected transactions through pre-validation and to deliver value to corporations looking for transparency of fees and better traceability on inbound and outbound treasury payments. With the launch of SWIFT Go, the foundation piece for real-time cross-border payments, the gpi model is also applied to low-value payments.
In the past 5 years alone, SWIFT has launched several new services and completed multiple proofs-of-concept, ranging from launching the first real-time cross-border payment to assessing the use of blockchain technology as part of the SWIFT network while implementing Financial Crimes and data analytics services.
The future of SWIFT
If you still think SWIFT is “just for cross-border payments” you might need to take a second look. SWIFT is the heart and soul of payments worldwide, and without access to it, any economy could easily collapse.
As a result of recent global events, interest in SWIFT and its functions in financial services has certainly grown. Banks and large corporations have relied on SWIFT for secure messaging since 1973, but it doesn’t often get public visibility. By consistently delivering efficient and secure payments, SWIFT has earned the trust of 11,000+ members. As long as it continues to listen to their needs and collaborate and innovate to provide new value, SWIFT will continue to grow and dominate payments worldwide.
Source: ibm.com
Thursday, 12 May 2022
Digital engineering is the answer when flawless, accountable production means life or death
Digital technology transformations have streamlined analog processes for decades, making complicated tasks easier, faster, more intuitive and even automatic. The modern car is the perfect expression of this idea. Cars produced in the last few decades are more than cars — they’re a bundle of digital processes with the ability to regulate fuel consumption, detect unsafe conditions, understand when the vehicle is coming close to a collision and ensure the driver doesn’t unknowingly drift out of their lane.
The array of sensors and actuators, cameras, radar, lidar and embedded computer subsystems in these vehicles can’t just be useful gadgets; they must flawlessly ensure the safety of the driver and passengers. These incredibly complex systems are often developed by different engineering teams or companies. Without the proper development processes, bugs can go unnoticed until after the model ships. For car manufacturers, ensuring that their systems are safe is a matter of life and death.
If a car manufacturer finds a flaw in the self-driving system only after the model has shipped, they face a clear crisis. There isn’t time to contact the dealers, to email drivers or to erect billboards warning of the flaw. The issue must be fixed immediately, or the car manufacturer could face irreparable damage. If the computer system was designed with a firm digital engineering foundation, the manufacturer could easily fix the issue by sending out a “cloud burst” to update every car on the network before the flaw becomes dangerous.
Digital product engineering enables complex, high-stakes development
The goal in digital engineering is to not only minimize flaws in every outgoing vehicle, but to establish a development environment to ensure that once a flaw is detected, it can be fixed quickly and safely. To achieve this, we recommend that companies embrace digital product engineering and digital thread technology. A digital thread is an engineering process whereby a product’s development can be digitally traced throughout its lifecycle, upstream or downstream.
Since the invention of digital technology, businesses have been using computers to automate shipping systems, supply systems and warehouse systems. As the power of that technology continues to grow, businesses are applying the same principles of automation to the development process as well.
Businesses can now create an easy-to-access digital repository for collaborators to work on or view. Updates to the product are made within that central source, ensuring everyone has access to the most up-to-date version of the product.
Digital product engineering is an evolving process, a future-state that organizations need to achieve to make the world a safer, more secure place. Digital engineering holds such promise that the US Government Department of Defense has stipulated in their digital engineering strategy that any subcontractors they work with must use digital engineering processes to ensure transparency, safety and accountability for their high-tech defense systems.
At the highest-level, digital engineering is a holistic, data-first approach to the end-to-end design of complex systems. Models and data can be used and shared throughout the development of the product, eschewing older documents-based methods. The goal is to formalize the development and integration of systems, provide a single authoritative source of truth, improve engineering through technological innovation, and establish supporting engineering infrastructure to ease development, collaboration and communication across teams and disciplines.
Digital thread can provide users with a logic path for tracking information throughout the systems’ lifecycle or ecosystem. By pulling on the digital thread, engineering teams can better understand the impact of design changes, as well as manage requirements, design, implementation and verification. This capability is vital for accurately managing regulatory and compliance requirements, reporting development status and responding quickly to product recalls and quality issues. In terms of digital engineering, a digital thread represents a significant role in connecting engineering data to related processes and people. But a digital thread is not plug and play; it’s a process that must be designed from the ground up.
The IBM digital engineering solution
To make it one step easier for your organization, IBM® Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) can establish the ideal base for your company to pursue digital engineering transformation. ELM is built from the ground up around the digital thread model. Each lifecycle application seamlessly shares engineering data with every other lifecycle application, such as downstream software, electronics and mechanical domain applications. ELM leverages the highly-proven W3C linked data approach using Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration (OSLC) adapters for both internal and external information exchange — the same approach used to seamlessly connect web applications across industries.
ELM leverages OSLC to connect data and processes along the engineering lifecycle. By enabling this standards-based integration architecture, engineering teams can avoid the complications inherent in developing and maintaining proprietary point-to-point integrations.
Lumen Freedom, a manufacturer of wireless charging units for electric vehicles, wants to provide an untethered world for electric vehicle owners. In pioneering this innovation, Lumen’s design management became increasingly complex and difficult to manage. To level up their product development goals, Lumen adopted digital engineering lifecycle management tools from ELM that allow them to capture, trace and analyze mechanical, hardware and software requirements throughout the entire product development process. “Given that DOORS® Next and ELM are essentially standards in the automotive industry, we chose IBM for our preferred toolchain,” says David Eliott, Systems Architect at Lumen Freedom.
ELM maintains a linked data foundation for digital engineering and provides data continuity and traceability within integrated processes. With global data configuration, engineering teams can define a consistent baseline and provide central analytics and reporting components. ELM fosters consistency across all data while providing an automated audit trail, ensuring ease of access to digital evidence for regulatory compliance.
Source: ibm.com
Tuesday, 10 May 2022
How Canada is growing its data economy
The data economy is booming. In 2021, IDC estimated the value of the data economy in the U.S. at USD 255 billion, and that of the European Union at USD 110 billion. In these and many other regions, growth in the data economy outpaces GDP. IBM has examined Canada’s particular potential for data leadership, with lessons for any other country hoping to compete in the data economy.
Will we get to CAD 1 trillion value of data in Canada before 2030? In mid-2019, Statistics Canada estimated that Canadian investment in “data, databases and data science” has grown over 400% since 2005. At an upper limit, the value of the stock of data, databases and data science in Canada was $217B in 2018, roughly equivalent to the stock of all other intellectual property products (software, research and development, mineral exploration) and equivalent to more than two-thirds the value of the country’s crude oil reserves.
As the world continues to rapidly change around us, ground-breaking opportunities are presenting themselves that will shift the fundamentals of how businesses, governments and citizens function. This shift will be supported by enormous amounts of data, regardless of the part of society in which these transformations take place.
What is the data economy?
The amount of data throughout the world has almost doubled in just two years, with growth expected to triple by the year 2025. With data’s unprecedented growth, important decisions will have to be made about how to use it; and these decisions will determine the commercial success or failure of the digital revolution.
The data economy is the social and economic value attained from data sharing. While data has no inherent value, its use does. When it is organized, categorized and transformed into information that can drive innovation, solve complex problems, create new products, or provide better services its value becomes apparent.
While data can solve critical challenges in our society, most of its value is inaccessible due to the siloed and fragmented nature of most data ecosystems. Governments cannot develop effective policies; business leaders are unable to fully tap their resources; and citizens are prevented from making informed decisions. Leveraging data to benefit society depends upon the amount of connections that we can form between contributors and consumers, among enterprises and governments. A prosperous data economy must be linked to intelligent governance, administered for the good of everyone.
Why does it matter?
1. Citizens can assume more control of their data, ensuring its appropriate use and security while benefiting from new products and services.
2. Businesses can customize their products to align with their clients and better manage regulations.
3. Governments can collaborate on national and international strategies to achieve optimum effectiveness on a global scale.
And what can it do for you?
The profound implications of well-managed global data exchanges illuminate the vision of a better world, opening the window to myriad possibilities:
◉ Fighting disease through shared research on diagnostics and therapeutics
◉ Identifying global threats and reacting to them quickly
◉ Deploying advanced applications to solve organizational issues, unlocking innovation
◉ Harnessing data to promote environmental health, prevent environmental degradation and protect at-risk ecosystems
◉ Coordinating data to benefit industrial sectors such as tourism or agriculture
Canada has the potential to create a world-leading data economy, positioning us to develop innovations that will allow us to compete globally. We have many advantages in our favour: a highly trained workforce strengthened by our skills-based immigration system; our government’s commitment to accountability, security and innovation; and our unique history, geography and public policies.Our success will depend upon a collective effort to promote engagement and facilitate the transition to a data-driven economy. Together with its financial investment, Canada must focus on cultivating data literacy among its citizens, as businesses increasingly embrace digitized platforms.
Fast-tracked by COVID-19, investment in data science has accelerated, alongside the proliferation of emerging technologies. By leveraging the opportunities in the rising data economy, Canada can unlock a trillion-dollar benefit within the next decade.
Source: ibm.com
Sunday, 8 May 2022
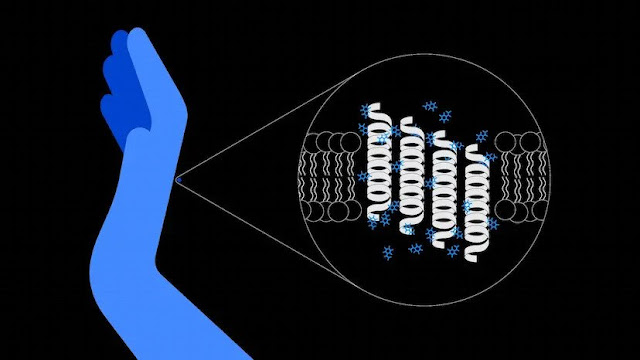
Computer simulations identify new ways to boost the skin’s natural protectors
Working with Unilever and the UK’s STFC Hartree Centre, IBM Research uncovered how skin can boost its natural defense against germs.
Simulating molecular interactions
A radical discovery process — and a map for hunting new bioactives
Saturday, 7 May 2022
Difference between AIX and IBM i
1. AIX :
AIX is a series of proprietary operating systems which is provided by IBM. AIX stands for Advanced Interactive eXecutive. Initially it was designed for the IBM RT PC RISC workstation and later it was used for various hardware platforms like IBM RS/6000 series, PowerPC-based systems, System-370 mainframes, PS-2 personal computers and Apple Network Server. It is one of the five commercial operating systems that have versions certified to UNIX 03 standard of The Open Group. The first version of AIX was launched in 1986. The latest stable version of AIX is 7.2.
2. IBM i :
IBM i is an operating system or operating environment which is provided by IBM. It provides an abstract interface to IBM Power Systems. It works through the layers of low level machine interface code or microcode that reside above the Technology Independent Machine Interface and the System Licensed Internal Code or kernel. It enables the IBM Power platform to support a wide variety of business applications and can co-exist alongside other operating systems. It is a closed source operating system. The first version of IBM i was launched in 1988. The latest stable version of IBM i is 7.3.
Difference between AIX and IBM i :
| AIX | IBM i |
| It was developed and is owned by IBM. | It was developed and is owned by IBM. |
| It was launched in 1986. | It was launched in 1988. |
| Its target system type is Server, NAS and workstation. | Its target system type are minicomputer and server. |
| Kernel type is Monolithic with modules. | Kernel type is Microkernel and Virtual machine. |
| Preferred license is Proprietary. | Preferred license is Proprietary |
| It is used for personal computers. | It is not used for personal computers. |
| It is used in computers of all companies. | It is majorly used in IBM devices. |
| File systems supported are NTFS, FAT, ISO 9660, UDF. | File systems supported are JFS, JFS2, ISO 9660, UDF, NFS, SMBFS and GPFS. |
Tuesday, 3 May 2022
How to win your SWIFT challenge
We are living in a cloud era, with new tools, programming languages, and technologies evolving at a much higher speed than even just 2 years ago. Workers need to refresh and resharpen skills on a regular basis. Financial institutions must embrace these changes and be prepared for the technological shifts and the innovative features needed to compete in the financial market.
New fintechs emerge every year with greater ideas and faster technologies. Initiatives like blockchain and real-time transaction settlements, Decentralized Finance (DeFi), and the Internet of Things (IoT) place pressure on larger institutions to ensure they move at the same pace and direction. It is challenging for these larger FIs to stay agile in the payments world when they are hindered by legacy technologies and the traditional ways of managing them.
Keeping up with SWIFT
If you are already in the financial sector, you likely have heard of SWIFT, also known as The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications. SWIFT is a global member-owned cooperative and the world’s leading provider of secure financial messaging services.
Today, as goods and services move more quickly and across greater distances, financial transactions need to move further and faster as well. SWIFT securely moves values around the world while meeting the high demands and standards for regulatory compliance. No other organization can address the scale, precision, pace and trust that SWIFT provides to its user community.
SWIFT continues to refresh and evolve its platform to ensure it remains modern, powerful, reliable and feature-rich. SWIFT regularly adds new innovative capabilities and functionalities, develops new forms of connectivity, eases service consumption, and ensures secure user access.
In addition, SWIFT constantly renews their product portfolio in response to the needs of their user community. They foster a culture of innovation to bring new offerings to market while preserving a no-risk approach to the maintenance and evolution of their mission-critical core.
The challenges for financial institutions to keep up with SWIFT are heavy and demanding, but they are also crucial for survival. FIs must move quickly to adopt all of SWIFT’s initiatives and embrace new changes with agility. What does this mean for our FIs?
Keeping up takes a heavy investment on the FI’s core platforms, infrastructure, and resources, which requires continuous learning and certification, operations excellence, improved skills to support new platforms, and tighter SLAs to guarantee a reliable service for their clients.
Client story: a turnkey solution from the IBM Payments Center™
One institution that met these challenges is an essential FI in the Canadian economic system. This FI once had a heavy on-premises SWIFT infrastructure with unsupported machines and operating systems and few skills to support application operations. In addition, there were SWIFT’s requirements to adopt new standards, to keep up with the SWIFT roadmap, ISO 20022 migration, and the frequent updates and patching to secure a sensitive cross-border payments platform. The FI also faced the increasing cost of support and operations needed for the latest infrastructure upgrades.
The IBM Service Bureau for SWIFT from the IBM Payments Center™ (IPC) was a turnkey solution to address this client’s challenge. Over the span of a year, the IPC built a dedicated SWIFT infrastructure into IBM’s private cloud, operated entirely by IBM and supported by SWIFT certified experts. No other SWIFT service bureau could offer a solution at this scale.
The solution consisted of deploying a fully redundant SWIFT infrastructure, with mission-critical components: SWIFT’s Alliance Connect Gold was deployed by IBM in multiple sites, and dual Alliance Access and Web platform instances were deployed in each site; hot standby cross-connect SWIFT instances were established; and fully redundant Backoffice connectors were implemented, with the entire setup guaranteeing a 99.99% uptime.The complete Customer Security Program (CSP), as prescribed by SWIFT, was an integral part of the solution. As a result, the client didn’t have to implement all the compliance controls themselves. Moreover, patches, new releases, and SWIFT standards deployments were fully managed by the IBM SWIFT team. All this was crowned with 24/7 fully managed operation and support. The CSP provided real value to the FI by reducing or eliminating many of the costly challenges they faced.
Knowing their core application is being handled with care, the client has regained peace of mind and is able to now focus more on its core business.
At the end of the day, FIs must choose their battles, and a technology-focused battle, with ever-increasing costs, demands and skills, isn’t easy. The IBM Payments Center’s deep experience in technologies and payments helps FIs across the world win at every scale.
Source: ibm.com