Thursday, 12 September 2024
How fintechs are helping banks accelerate innovation while navigating global regulations
Tuesday, 19 September 2023
How generative AI is revolutionizing supply chain operations
A new and exciting wave of disruption
Pivoting from ideation to action
IBM’s supply chain AI journey
Tuesday, 8 August 2023
The Orion blockchain database: Empowering multi-party data governance
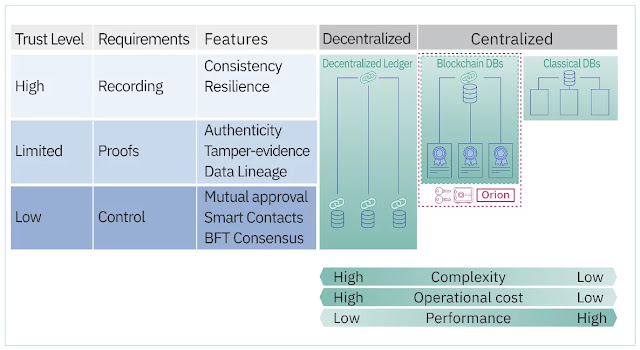
Importance of trust in business ecosystems
Understanding trust requirements
Technological choices to address the trust gaps
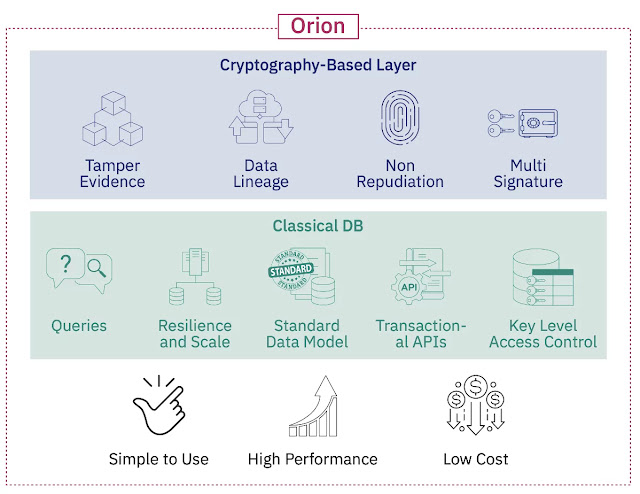
Meet Orion: A centralized blockchain database with multi-party data access control
Key applications lead to valuable solutions
Thursday, 21 April 2022
Why central banks dislike cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies, often depicted as an escape from fiat currency and legacy banking, have become a constant focus of bank and government activity. The most recent Executive Order from the U.S. President is just one example of governments carefully considering how to deal with cryptocurrencies. With all the news, it’s easy to lose sight of the fundamentals of monetary policy and currency, and why cryptocurrencies (or “cryptos”) are not a likely replacement for fiat currencies.
In 2021 the Bank of International Settlements (which is owned by, and provides financial services to, central banks) commissioned an academic research paper entitled “Distrust or speculation? The socioeconomic drivers of U.S. cryptocurrency investments.” The research found that crypto investors were more likely to be digital banking users, male, young, and educated. More surprisingly, it found that cryptocurrency investors and users were not motivated by a distrust in traditional banking and payment services. This touted raison d’être for Bitcoin and other early cryptos seems to be a myth.
Crypto’s limits as a form of payment
Of course, the popularity of cryptos has partly been driven by high valuations and volatility, attracting attention from traders, the media and the public. But this volatility makes cryptos less than ideal for payments. Companies like Tesla and Amazon, after initially stating they would accept some cryptos as currency, have since backtracked. Why would they want to accept a currency whose value can fluctuate so dramatically on a daily basis?
Why, indeed, would anyone? Will cryptos find their way into mainstream payment systems, or will they remain a speculative investment? Much of the answer rests on an understanding of how governments, regulators, and central banks act to protect their economies and citizenry. Why “protect”? Let’s explore that with a brief look at the role of central banks.
How unstable crypto prices challenge central banks
Key roles of any country’s central bank are to:
1. Govern the safety and soundness and stability of the economy and its systems (the authority for this varies by country, but for the purposes of this piece, it’s a sufficient generalization)
2. Help to ensure the country is a safe place in which to invest for the longer term by controlling inflation
The most direct method of controlling inflation and the relative value of a currency is by setting the interest rate provided to commercial banks for their deposits and borrowings from the central bank. This largely determines the interest provided by commercial banks to their depositors and borrowers, which in turn has a direct effect on economic behaviors such as spending and saving.
Some central banks set an overt inflation target: the Bank of Canada, for example, has set one since 1991, and it resets that target with the federal government every five years. Some governments and central banks tie their economy to another economy by setting a fixed exchange rate between their fiat currency with another, such as USD or EUR. Either way, the goal is to control inflation by managing the value of the currency. A central bank’s power to control a fiat currency is largely derived from the sovereignty of the country in which it operates, with a taxable population that supports the economic and banking systems and governing structures.
Now if you, as a central bank, don’t control the value of the currency used by your population, you can no longer control inflation or the safety, stability and soundness of your economic and financial systems. Cryptos are not directly affected by any particular country’s interest rates, at least not more than myriad other factors that send their values swirling.
For a central bank, if the actors involved in valuing and distributing the currency are beyond your control, then you’ve essentially ceded control of monetary policy to those actors and their activities. The system will become susceptible to rapid inflation or deflation. The same unit of cryptocurrency may buy a smartphone today and a sandwich tomorrow. Individuals and businesses will begin to distrust the system, and the economy will suffer.
The potential of centrally backed stablecoins
This is not to say that the technology used by cryptos cannot also be used by central banks to provide, regulate or monitor stable digital currencies for the populations and economies they protect. Central banks and governments, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, are currently exploring central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). Some have worked for several years with the cooperation of commercial banks. The topic is now prominent for many legislators and bureaucrats involved with financial systems. In January 2021, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency in the United States released regulatory guidance around the use of blockchain technologies in financial systems, and some central banks have already established proof-of-concept activities with central banks. The most recent U.S. Presidential Executive Order, and the two bills recently introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate, also demonstrate the concern governments have about digital assets and currencies, and they attempt to standardize definitions and protections. Many believe it’s only a matter of time before currency does become purely digital.
CBDCs would behave differently from the most popular existing cryptos: if they are directly tied to a fiat currency, like a “stablecoin,” their value remains as stable as the fiat currency. If they can easily be traced from user to user, they are no longer viable for money laundering, underground economic behaviors, or the financing of other illicit activities. While the usage of cryptos for illegal purposes is perhaps overstated (usage of cash for criminal activities is still more prevalent), there is a considerable appeal for central banks and governments in luring away legitimate crypto users and devaluing less traceable cryptos.
When you take away the pundit opinions, the recent Executive Order from the U.S. President is really asking for some thoughtful consideration of how digital assets should be regulated. With respect to cryptos, governments are in a tricky position: since so many people have invested (some of them their life savings) in cryptos or other digital assets, governments now have to consider how to protect their citizenry. If governments do nothing to regulate the cryptos market, and they instruct or allow central banks to issue their own CBDCs, the resulting impact on cryptos could be catastrophic for some parties, and could have an impact on the economy as a whole. That impact could sway the electorate to make certain decisions about a government they don’t see protecting them (even if from themselves). If the government does regulate cryptos with a heavy hand, and the valuations subsequently decline, the impact to individuals and the economy could be similarly catastrophic and electorate-swaying.
Notwithstanding the regulatory issues regarding cryptos, banks could gain other benefits by tracking currency flows and usage. Certainly, it could help the central banks’ objectives of monitoring and influencing economic growth.
How will this affect the current crop of several thousand cryptocurrencies? Only time will tell. If you like speculative, risky investments, cryptos may be for you, but choose carefully. The day may come when the actions of those with the mandate to protect their sovereign economies and markets will render some cryptos irrelevant or of limited value, and only good as relics for hobbyists and historians.
Source: ibm.com
Saturday, 9 January 2021
Blockchain and sustainability through responsible sourcing
Mining for cobalt, an essential raw material for lithium-ion batteries, carries a high cost in human suffering. More than 60 percent of the world’s supply comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), with about 45 percent coming from large-scale mining operations. The remaining 15 percent comes from small-scale mines in the DRC, where children and adults labor under harsh and dangerous conditions to extract ore by hand.
It’s those working conditions, along with environmental damage to areas mined, that have focused the world’s eyes on the high-profile automotive and electronics industries. Their products — electric vehicles (EVs) smartphones and laptops — depend on lithium-ion batteries, and thus, cobalt.
What’s driving sustainable sourcing initiatives
Companies that take sustainability and social justice seriously work to keep cobalt mined by hand out of their supply chains. Similar concerns hold true for other minerals that pose responsible sourcing risks, including lithium, nickel, copper and the “3TG” group (tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold), and for materials that create a hazard for the environment when disposed of incorrectly.
Deploy the IBM Blockchain Platform across multiple environments
The drivers for responsible sourcing of raw materials are strong, ranging from corporate governance to consumer, shareholder and other stakeholder demands to scrutiny from governments, regulatory bodies, financial markets and NGOs. However, until recently, proving responsible sourcing to all these interested parties was an elusive goal, posing significant reputational, legal and commercial risks.
The benefits of blockchain for responsible sourcing networks
Today, the Responsible Sourcing Blockchain Network (RSBN), built on IBM Blockchain Platform and assured by RCS Global Group, is providing the transparency, trust and security that are needed to demonstrate responsible sourcing for cobalt. What’s more, the underlying infrastructure that we’ve built for RSBN can be used to jump-start any sustainable sourcing initiative.
The proven benefits of using blockchain technology for sustainable sourcing networks include:
◉ An immutable audit trail that documents proof of initial ethical production of a raw material and its maintenance at every transfer step from mine to end manufacturer
◉ Secure, tamper-evident storage of provenance information and certificates of responsible production
◉ The ability to share a proof of fact while protecting confidential or competitive information
◉ Decentralized control so no single entity can corrupt the process, promoting trust
◉ Lower costs through digitization of a paper process, potential reduction in audits and lower transaction costs
◉ Scalability to accommodate new participants and new industries
Blockchain and RSBN: How it works
Traditionally, miners, smelters, distributers and manufacturers rely on third-party audits to establish compliance with generally accepted industry standards. For RSBN, RCS Global Group provides this assurance through its mineral supply chain mapping and auditing practice, assessing network participants against standards and best practices set by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI).
RSBN uses blockchain’s shared, distributed ledger to track production from mine to battery to end product, capturing information on the degree of responsible sourcing at each tier of the supply chain. Downstream companies can access the verified proof that they support and contribute to responsible sourcing practices, which they can then share with auditors, corporate governance bodies and even consumers.
At every step, participants control who is allowed to see what information. Once added to the ledger, certifications and other documents cannot be manipulated, changed or deleted. These properties make blockchain a trusted platform for sharing data across different companies while helping prevent fraud.
Delivering business value across the supply chain
Networks such as RSBN encourage and enable collaboration between suppliers and customers across complex mineral and other conflict-sourced raw material supply chains, with business value accruing to all that participate. For example, here are benefits realized by RSBN participants.
Automotive manufacturers are gearing up to introduce many more electric vehicles (EVs) into the marketplace over 2021 and 2022, creating new demand for li-ion batteries and the cobalt they require. By engaging in responsible sourcing initiatives like RSBN, they can market their products as sustainably produced as well as sustainable on the road. Responsible cobalt sourcing also contributes to corporate citizenship efforts related to fighting poverty, supporting human rights and preventing environmental degradation.
Mines and smelters sit at the top of the supply chain, where responsible sourcing efforts begin and where the real challenges lie. Keeping hand-mined cobalt out of product batches requires process changes, financial investments and a commitment to fight corruption. By demonstrating their results through audits and certifications, these companies are positioned for favored status as suppliers to battery manufacturers.
Consumers have spoken. In a recent IBM study, 77 percent of consumers surveyed said that buying from sustainable or environmentally responsible brands is important. EVs, smartphones and laptops are high-visibility products whose value is closely tied to their rechargeable, long-lasting li-ion batteries. Being able to demonstrate responsible sourcing can help win customers, establish reputational value and prevent backlash such as legal action.
Get started quickly on your responsible sourcing solution
RSBN is a ready-to-join network built on IBM Blockchain Platform and assured by RSC Global. RSBN founding members include Ford Motor Company, Volkswagen Group, global battery manufacturer LG Chem and cobalt supplier Huayou Cobalt. Volvo Cars, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles and other companies that operate in “conflict sourced” minerals supply chains are also members.
Companies that want to make sure the raw materials they use have audited and documented responsible sourcing standards confirmed can join RSBN either as an individual company or with their whole supply chain and begin realizing value quickly. Alternatively, IBM Blockchain Services can leverage the assets and infrastructure that underpin RSBN to co-create a responsible sourcing network for other industries and raw materials. Talk to us today about how you can get started demonstrating your organization’s responsible sourcing compliance.
Source: ibm.com
Sunday, 25 October 2020
Expanding choice for blockchain workloads with R3 Corda Enterprise on IBM LinuxONE
News from R3’s CordaCon
Thursday, 9 July 2020
3 critical responsibilities of digital asset custodians
At Hex Trust we provide an enterprise platform which allows financial institutions to use blockchain to integrate digital assets into their business operations in a highly secured, scalable and compliant solution.
While we agree with market estimates that widespread implementation could still be several years away, Hex Trust believes that the size of the digital assets market could reach US$ 10 trillion by 2023, causing a big shift in the overall structure of financial markets. Banks and other financial intermediaries will soon be forced to devise and implement new digital asset strategies.
Custodians: the foundation of a successful digital asset solution
The role of custodians will be a critical building block for the new financial markets infrastructure and will be necessary for the widespread adoption of digital assets. We believe there are three critical responsibilities for digital asset custodians: safekeeping, connectivity and compliance.
Safekeeping
Securely custodizing digital assets protects the private keys and develops secure workflows to support transactions in and out of custody (deposits and withdrawals). So far, custodians have relied on cold wallets created and managed in air-gapped environments to provide the clients with an acceptable level of security. Conversely, most hacks have concentrated on hot wallets, used to provide clients with quick access to their assets. Multi-signature wallets and wallets based on threshold algorithms such as state space search (SSS) and model predictive control (MPC) mitigate some of the risks of hot wallets. In addition to storage of the private keys, custodians must build their technology architectures to manage cybersecurity risks when interfacing with a public blockchain to facilitate transfers of these assets.
As the blockchain market becomes institutional, the current wallet implementations will not be scalable enough to cater to the requirements of financial intermediaries. A new approach will be required to offer custody solutions which can scale and process thousands of transactions per second with the necessary levels of security.
Hex Trust’s custody platform, Hex Safe™, was specifically engineered leveraging IBM Hyper Protect Virtual Servers and IBM LinuxONE to enable trusted cryptographic transactions and to deliver the highest level of security and scalability. In addition to a holistic protection compliant to FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standards) 197 and FIPS 140-2 Level 4 HSM (Hardware Security Module) standards, the IBM Z environment has memory enclaves with common criteria EAL (Evaluation Assurance Level) 5+ rated separation between partitions. Hex Safe integrates additional security measures to enhance the security of assets such as automatic encryption, hardware-bound signing, and immutable customized compliance workflows, protected by tamper-proof secure boot and Secure Image Build, defend the system from malware contamination or coding attacks.
Connectivity
At Hex Trust we believe that a key responsibility of digital asset custodians lies in simplifying the underlying complexities of blockchain technologies and creating a standard access layer to connect capital and service providers across the ecosystem. This is a critical building block to extract the maximum value that blockchain networks can offer to its users and an opportunity to design a new financial market structure fundamentally different from the current one.
Hex Trust is spearheading this transformation by providing its clients an open platform that can be used to securely store assets and to access services offered in the digital asset ecosystem, focusing on integrating brokers, prime brokers, exchanges, lending and borrowing platforms, staking solutions and other custodians.
In addition, Hex Trust is committed to providing a secure bridge between the traditional financial world and the new digital asset ecosystem, allowing banks and other traditional financial institutions to access and serve clients in the digital asset space. As an example of this effort, Hex Safe integrates a SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) interface to create a seamless communication channel with traditional financial institutions.
Compliance
Following the dramatic rise in cryptocurrency investments and trading activities over the last few years, regulators are setting their sights on this growing part of the financial services industry. An example of the regulatory interest is the new guidance published in June 2019 by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) on how its 37 members should regulate cryptocurrency exchanges. Unlike regulated financial institutions, most cryptocurrency exchanges, and other digital asset operators, do not currently have a legal or technological framework to obtain, hold and transmit identifying information for their transaction counterparties. In addition, while there has been clear progress in various jurisdictions with respect to digital assets, service providers operating in different countries have different regulatory expectations with very limited global consensus on cross-border activities.
At Hex Trust, we believe that digital assets custodians will play a critical role in facilitating the adoption of regulatory and compliance frameworks in the industry. This role consists of various responsibilities including monitoring clients’ transactions to prevent AML/CTF (Anti-Money Laundering/Counter-Terrorism Financing) activities, reporting identified and transaction information to regulators, protecting clients’ data and providing clients and regulators with tools to perform their compliance activities.
Hex Safe has been specifically designed to meet the complex compliance requirements of our target clients — banks and other financial institutions. Examples of features include on-chain and off-chain account segregation, full audit trails, integrated AML/KYC (Anti-Money Laundering/Know Your Customer) tools to prove ownership and source of funds, and regulatory and internal reporting capabilities. Further, data privacy regulations can add additional levels of complexity, as custodians must be able to collect and transmit data without accessing and storing sensitive third-party data.
In line with our collaborative approach to the digital asset market, Hex Safe has already integrated third-party tools to enhance our blockchain analytics functionalities, with a long term objective of connecting various compliance platforms to satisfy the requirements of our clients and the jurisdictions they operate in.
Looking towards the future of the digital asset market
As blockchain technology and digital assets become mainstream, the role of the custodian is evolving from simply providing a secure wallet to providing bank-grade security and transactional capability, securely connecting services and capital across the market, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and legislations in various jurisdictions. These responsibilities pose a complex challenge to invested entities and will ultimately define the future of the market infrastructure. Hex Trust, with IBM infrastructure, is well-positioned to lead the transformation in this area and offer digital assets players the first bank-grade solution to access the digital asset market.
Thursday, 25 June 2020
IBM and Verum Capital help businesses leverage blockchain
The rise of the digital economy
According to Research and Markets, the global digital asset management market is growing at 16.5 percent to reach $8.5 billion by 2025. In Switzerland, two banks are now fully licensed to offer blockchain-based financial instruments and traditional banks are increasingly offering crypto services. In the DACH region, more than 50 banks have applied for a license to offer similar services.
More and more, leading financial institutions are bringing traditional investment products onto blockchain. This shift toward decentralized finance is important for the future of the digital economy. By offering blockchain-based financial products, financial institutions can grow business through inclusion. At the individual level, blockchain-based services can support the unbanked but also the micro-investor who can gain access to the rate of return typically reserved for institutional investors with large sums of money. At the organizational level, financial products that are built using the blockchain become affordable and flexible enough to serve the SME segment. Now small businesses can also benefit from bond issuance on blockchain, for example.
Digitizing assets
Traditional company shares, bonds, loans or non-traditional and non-bankable assets such as artworks, real estate properties, private securities, even gold can be digitized, tokenized, and traded on a variety of platforms. An advantage of tokenizing assets is that it creates a fractional ownership scheme for physical assets that had previously been considered indivisible. The underlying asset could then be offered to a larger number of buyers who have increased liquidity on the secondary market. Tokenization allows the digital economy to become much more efficient, transparent, and liquid, while it also becomes a more inclusive marketplace.
Key success factors
Storing and trading digital assets securely using blockchain is a step forward in unleashing the transformative potential of the digital economy.
There are two key success factors for the widespread adoption of digital assets: hypercritical availability and scalability, as well as simultaneous industry-leading security.
Until now, this trade-off has presented a significant obstacle. Users had to choose between availability and security when handling their digital assets. IBM is solving this trade-off for financial services providers through cutting-edge digital asset custody that makes the location of the asset irrelevant (no matter where the asset is actually stored). The technology has incredible potential to improve digital asset availability without sacrificing security.
Verum Capital and IBM — strong synergies
IBM’s digital asset custody solutions are the basis for the collaboration with Verum Capital. Together, Verum Capital and IBM can offer clients highly secure and scalable digital asset infrastructure solutions, as well as the essential advisory services that will enable them to develop new business opportunities using blockchain.
As the leading blockchain advisory, Verum Capital is joining IBM’s unique ecosystem to ensure that these institutional-grade digital asset services can best be used in the financial services sector.
Since 1977, tens of trillions of dollars of wealth have been secured using hardware security modules (HSMs) invented by IBM. Featuring hardware security modules, IBM LinuxONE servers, for example, enable pervasive encryption of all application data in-flight and at-rest. They run IBM Hyper Protect Virtual Servers, a solution that provides a secure computing environment for highly sensitive data.
Once again, IBM is at the forefront of a technological solution for wealth storage and transaction, and together IBM and Verum Capital are the perfect fit for the positioning of this next generation technology.
Based on our extensive experience working on strategic blockchain projects within the financial sector, we know how incredibly valuable it is for clients to have the choice to deploy a solution on-premises, as part of a private cloud environment, or as a service, allowing digital asset and blockchain firms to scale with the growing demand.
The essential infrastructure that IBM continues to develop is a very valuable building block for our team of blockchain consultants. When we advise our clients, develop pilot projects, and manage full-scale implementations of blockchain technology, we choose to work with IBM’s infrastructure and products because businesses are very comfortable relying on IBM.
Thursday, 28 May 2020
No two supply chains are the same – IBM Sterling has a platform for that
At IBM, we believe the only way to create end-to-end supply chain solutions is with an open platform that you can extend and enhance. This platform should provide building blocks so you can customize and configure solutions and bridge to other networks and services involved in the supply chain – and enable you to bring in data and insights from other domains to solve supply chain problems unique to your business.
What open means for supply chain
This commitment to open technology is in our DNA and that’s why I’m excited to tell you about the new IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite that we’re launching today. It’s part of our broader multi-enterprise business network (MEBN) strategy that acknowledges there are many types of networks and applications that must work together across different enterprises – with applications and expert services on top of data to bring added value – to not only solve problems but get ahead of them.
As part of the launch, we’re introducing the Sterling Developer Hub and Developer Advocacy Program to provide support across the entire development lifecycle and as you engage in the ecosystem.
How open works for you
The IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite delivers the following new extension points:
◉ Business service creation with public APIs. You can access public APIs for data ingest and query. A canonical map for data insulates the services from the particulars of the data origin, and new data origins don’t require changes to your applications.
◉ Open AI to build your own AI agents. The IBM Sterling Supply Chain Business Assistant gives you access to our AI agents, which are pre-trained in supply chain, as well as the ability to build your own supply chain business agents and introduce machine reasoning skills against external data sources. This allows you to teach the AI platform about problem domains specific to your supply chain.
◉ Assets for interconnecting with API-driven systems. Most new apps, services and networks are API-driven. As part of our network-of-networks strategy, the developer platform has iPaaS-based reusable assets to help you create the connective tissue to interconnect with other applications and services that are important to your supply chain.
◉ IBM Cloud Paks to run services wherever your business is. You can use the IBM Cloud Pak for Data to host custom analytics, AI and data science services using our InfoHub as a data source. You can also use the IBM Cloud Pak for Integration to interconnect your networks with other networks and systems. With Red Hat OpenShift you can run these Cloud Paks anywhere – in any cloud or on premise.
Monday, 27 April 2020
Fueling the next-generation of supply chains
Despite enormous investments of time, budget and resources, some first-generation digital supply chains are still optimized in functional silos. Collaboration across functions and organizations for them would still be plagued by traditional manual processes. And supply chains of that type could still be struggling to meet the needs of the business and the expectations of customers.
The next chapter of digital transformation will require supply chains that are dynamic, responsive and interconnected across ecosystems and processes. Moving forward, you will need to take even bolder strides to drive efficiencies and be resilient to disruptions.
The ultimate goal? Build intelligent, self-correcting supply chains that deepen your competitive differentiation today and are designed for whatever the future holds.
What smart means for supply chain
That’s why I’m thrilled about the IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite that we’re launching today. It’s an open, integrated platform with embedded Watson AI and IBM Blockchain that easily connects to your supplier and customer ecosystem. It helps you address persistent supply challenges by providing end-to-end visibility, real-time insights and recommended actions to turn disruptions into opportunities for customer engagement, growth and profit.
How smart works for supply chain
The IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite helps you build an intelligent, self-correcting supply chain with:
◉ Real-time intelligence and actionable recommendations. Applications and control towers, embedded with AI and trained in supply chain, provide end-to-end visibility, real-time alerts and recommendations that can be automated for self-correcting actions to help drive better business outcomes. Clients using individual Sterling applications, such as IBM Sterling Fulfillment Optimizer with Watson, in their supply chains today have lowered shipping cost per order by an average of 7 percent. IBM also used these capabilities in its own global supply chain to reduce disruption mitigation time from days to hours, becoming 95 percent more efficient at tackling recurring supply chain challenges.
◉ Trusted connectivity – built to scale, backed by IBM Blockchain. Our blockchain-enabled, multi-enterprise business network provides frictionless, secured connectivity and collaboration with customers, partners and suppliers. You can quickly engage with more than 800,000 preconnected trading partners executing 3 billion transactions a year.
◉ Open to developers to create tailored solutions. The IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite allows systems integrators and developers to build, extend and integrate tailored supply chain solutions that can interoperate with other business networks and applications. It also enables you to bring in third-party data so that all connected applications and networks can benefit from it. The Suite’s Developer Hub provides a global community of developers, open-source programs, and a library of knowledge resources to help solve your unique supply chain challenges faster.
◉ Hybrid-cloud integration to extend existing supply chain investments. Instead of requiring time-consuming and expensive migrations, the Suite’s enterprise-ready containerized software, along with IBM Cloud Paks, allows you to extend the value and reach of your legacy applications and data. This hybrid approach means you have the freedom to choose where to run your workloads and the ability to link them to value-added services in the IBM Sterling Supply Chain Suite. For example, IBM Sterling Order Management containers for Red Hat OpenShift will allow you to continue to run your software in their own datacenter – or in any cloud.
The bottom line: When you have greater transparency and a better understanding of what’s happening across your supply chain – coupled with intelligent applications for key supply chain activities – you can radically improve efficiencies. Achieve lower cost to serve with less chance of over or under correction. And make more informed decisions faster. Quite simply, you deliver better business outcomes.